Utilization of Monitoring Technology for
Friction Stir Welding and Friction Stir Processing
Burrs and flash occur
at the joint location,
affecting quality.
Probe wear is severe,
making tool costs a significant burden.
The appropriate tool and joining conditions
for new materials and new shapes
are unknown.
Efficient testing is not possible
because the joining mechanism has not been elucidated.
Due to many unknown factors, the number of parameters and tests increases.
I know improvement and investigation are necessary, but…
We don’t have enough time, staff, or equipment for testing…
We lack the equipment or know-how for evaluation…
We quantitatively measure and **visualize** tool wear, temperature of the probe tip and shoulder during joining, workpiece surface temperature, observation of defect status after joining, and spindle load, among others, to support the selection of optimal joining conditions.

FSW Evaluation Testing Services
Tool Production
Tool production
We can handle FSW tool production, leveraging our core technology in precision machining.
We also propose tool materials and shapes according to the joining material and application.
Tool material track record: SKD, Ni-base alloys, Cobalt alloys, Tungsten Carbide, etc.



Tool Temperature
Tool temperature
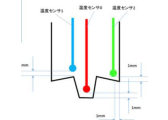
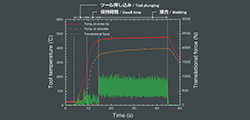
Real-time measurement of tool temperature and force during joining is possible using our proprietary product, MULTI INTELLIGENCE®i-stir!
Simultaneous measurement at three points can be utilized for heat input analysis.

Confirmation of Joining Quality
Checking the joining quality
We can handle various light metal materials and confirm the quality of the joint surface after welding.
We are also actively researching dissimilar material joining.
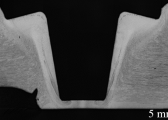
 Example of OK weld A5083 5t
Example of OK weld A5083 5t Example of NG weld A5083 5t
Example of NG weld A5083 5t Dissimilar Joining Example (Mg alloy + A6061)
Dissimilar Joining Example (Mg alloy + A6061)Observation of Defect State After Joining
Observation of defect state after joining
Defect status after joining can be confirmed using an X-ray inspection device!
By measuring the temperature during joining, the cause of defect occurrence can be investigated.
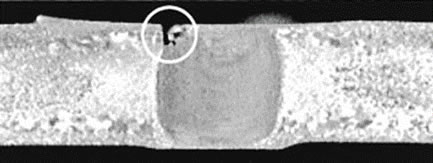 (a) External Defect
(a) External Defect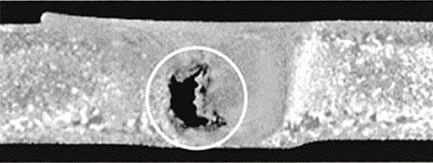 (b) Internal Defect
(b) Internal Defect (c) Underside Defect
(c) Underside DefectExample of Test Scenario
demonstration

Equipment for FSW Evaluation Testing

Contract testing can be performed using Hitachi equipment.
Furthermore, experts knowledgeable in FSW are on staff, allowing for more efficient testing.
Preheating Test for High-Strength Materials

FSW testing after preheating the joining material with a high-temperature machine is possible.
*Up to 200°C
Preheating can eliminate the temperature difference between the joining metal and the base material, avoiding defects (cracks, distortion, etc.) caused by heat effects. This also allows for friction stir welding of castings, etc., where the above factors must be considered.
We will explain FSW (Friction Stir Welding),
focusing on our monitoring technology.
For example, we respond to
requests like these.Request Order
- We have no track record within the company and no precedent, so it’s difficult to get started with testing.
- There are few organizations to consult with regarding the appropriate tools and joining conditions for new materials and new shapes.
- The joining mechanism has not been elucidated. We cannot assemble an efficient test plan.
- There are few opportunities to learn FSW joining theory with practical exercises.
Flow until Order / RequestFlow
- We accept consultations by phone and email
- First, please feel free to contact us by phone or email.
We will respond quickly.
- We will conduct a hearing and ask about your requests
- We will coordinate the testing specifications through meetings either by visiting or using a web conferencing system.
We will submit a quote based on the testing specifications.
- Test attendance is also possible
- If you actually place an order, you can attend the testing at the Okayama Research and Development Center.
Please feel free to contact us.
- TOP
- Business Introduction
- FSW Evaluation Testing Service

